What is a system design interview?
- In such kind of an interview, you are given a real-world problem and you are expected to come up with the required design for it.
- Since no system in this world is best, so you are expected to come up with the tradeoffs of your design. Like where a design will work well and where not. Its pros and cons.
- One of the major goals of system design interviews is to see whether candidate is able to identify these tradeoffs and fix cons.
High level design interviews:
- Here we talk about the system at high level. Meaning at services and architecture layer. Like:
- How will you structure your services?
- How are you deciding on your data storage layer?
- Which database are you planning to use and why?
- What all different components are you using like Kafka, Redis etc. depending on the given problem.
- Goal of this round is to evaluate whether the candidate is able to come up with the scalable and highly available system or not. Here scale is discussed in terms of number of users. Like will your system still work if load increases 10x or 100x?
- Expectations:
- Requirement Gathering and defining system constraints
- Identifying core system components.
- Component diagram - Explain responsibility of each component
- Associating Components and defining high level flow of various use cases.
- Design Considerations like fault tolerance, scalability, concurrency control, etc.
- More details on system design interviews you can find in this video: https://youtu.be/zkVll74UwGY
Example problems:
Design a system like BookMyShow / Instagram / URL Shortener / parking lot / CricInfo / Order Management System / distributed job scheduler / Bus scheduling system / ticket booking system / system to handle flash sales / Netflix / Access Management System / multi player game / Cab OR bicycle booking / railways Cloak Room / / Payment mechanism / Read Receipts mechanism in WhatsApp / price automation system / voice assistant used in mobile / event booking system / Generation of unique URL / leader board / MP3 player / file conversion tool / LRU Cache / torrent Client – For down loading files from Internet And many more. Beauty of system design problems is that they are infinite.
High-Level Design Learning strategy:
- Learn in depth concepts: Learning concepts is very important first.
- Different ways of achieving scalability
- Partitioning and sharding are very important here.
- How to achieve high availability.
- Replication
- Quorums
- Leader Election
- Replication
- Resource for both of these above: Book - Designing data intensive applications.
- Different ways of achieving scalability
- Learn about important components of backend systems:
- There are some very important components which are used in almost all the backend systems we create. Learn about them in depth next. Those components are:
- Databases: Both SQL and NoSQL. Learn when to you which one and why.
- Queues: Kafka etc.
- How they are used.
- What are some patterns which are solved by them and why queue is helpful for those patterns.
- How Kafka works internally. How does it provide scalability.
- How Kafka provides ordering.
- Caches.
- Blob store like s3.
- Resource: These above components are open source components, so you will be able to find documentation on their websites etc from where you should learn how they work behind the scenes. This will help you to relate the theoretical concepts you read previously. Like how they are implemented practically.
- There are some very important components which are used in almost all the backend systems we create. Learn about them in depth next. Those components are:
- Practice: Then try to practice building some practical systems by yourself. You can also try to look through some videos of how to build practical systems.
Steps in a High-Level Design interview:
- Step 1: Outline use cases, constraints, and assumptions
Gather requirements and scope the problem. Ask questions to clarify use cases and constraints. Discuss assumptions. It’s important to know what sort of design interviewer is looking for, so don’t assume anything. Clarify everything by asking questions.
- Who is going to use it? Who is the customer?
- How are they going to use it?
- How many users are there?
- What does the system do?
- What are the inputs and outputs of the system?
- How much data do we expect to handle?
- How many requests per second do we expect?
- What is the expected read to write ratio? As you keep asking questions, keep maintaining a list of the requirements. You are sort of wearing a hat of product manager here to finalize a very basic PRD.
- Step 2: Create a high-level design
Once you have good idea of the requirements you are going to solve for, start by outlining a high-level design with all important components.
- Sketch the main components and connections: A great way to do this is to draw shames to represent different software components and data sources and then arrows connecting them to show various services, APIs, databases, queues, caches, etc. depending on the problem you are solving. These arrows will show how your components are interacting with each other.
- Justify your ideas
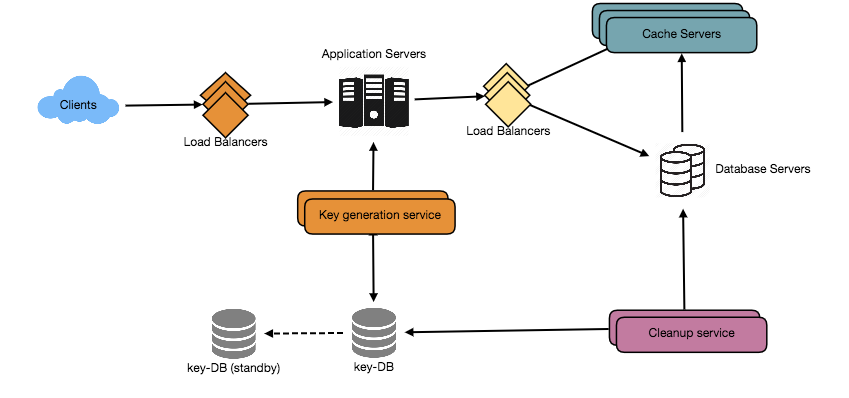
- Step 3: Design core components
Dive into details for each core component. For example, if you were asked to design a url shortening service, discuss:
- Generating and storing a hash of the full URL
- MD5 and Base62
- Hash collisions
- SQL or NoSQL
- Database schema
- Translating a hashed URL to the full URL
- Database lookup
- API and object-oriented design Basically, whatever is core to the problem, it’s the time to dive deep into that.
- Generating and storing a hash of the full URL
- Step 4: Scale the design
Identify and address bottlenecks, given the constraints. For example, do you need the following to address scalability issues?
- Load balancer
- Horizontal scaling
- Caching
- Database sharding Discuss potential solutions and trade-offs. Everything is a trade-off. Address bottlenecks.